Linux vs Windows, It’s time to make the big switch out of your Windows or Mac OS operating device.
Mac OS makes use of a UNIX middle. Your transfer from Mac OS to Linux will be fairly clean.
It’s the Windows customers who will need a few adjusting. In this tutorial will introduce the Linux OS and evaluate it with Windows.

In this tutorial will introduce the Linux OS and compare it with Windows.
-
- Windows Vs. Linux: File System
- Linux Types of Files
- Windows Vs. Linux: Users
- Windows Vs. Linux: File Name Convention
- Windows Vs. Linux: HOME Directory
- Windows Vs. Linux: Other Directories
- Windows Vs. Linux: Key Differences
Windows Vs. Linux File System
In Microsoft Windows, files are stored in folders on different facts drives like C: D: E:
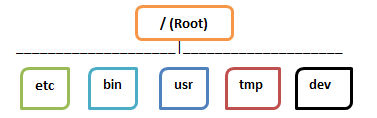
But, in Linux, documents are ordered in a tree structure starting with the root directory.
This root directory can be taken into consideration because the begin of the file device, and it further branches out numerous other subdirectories. The root is denoted with a ahead cut back ‘/’.
A fashionable tree document gadget for your UNIX may additionally appear like this.
Types of Files
In Linux and UNIX, the whole thing is a document. Directories are documents, documents are files, and devices like Printer, mouse, keyboard and many others.Are documents.
Let’s inspect the File kinds in more detail.
General Files
General Files also called as Ordinary files. They can comprise image, video, software or certainly text. They can be in ASCII or a Binary layout. These are the maximum typically used documents with the aid of Linux Users.
Directory Files
These files are a warehouse for different record types. You may have a listing record inside a directory (sub-listing).You can take them as ‘Folders’ observed in Windows working machine.
Device Files:
In MS Windows, gadgets like Printers, CD-ROM, and hard drives are represented as drive letters like G: H:. In Linux, there are represented as documents.For instance, if the primary SATA hard power had 3 primary walls, they would be named and numbered as /dev/sda1, /dev/sda2 and /dev/sda3.
Note: All tool files reside inside the directory /dev/
All the above record kinds (consisting of devices) have permissions, which allow a person to examine, edit or execute (run) them. This is a powerful Linux/Unix function. Access regulations may be carried out for one of a kind kinds of customers, with the aid of changing permissions.
Windows Vs. Linux: Users
There are 3 sorts of users in Linux.
- Regular
- Administrative(root)
- Service
Regular User
A normal person account is created for you when you install Ubuntu to your gadget. All your documents and folders are saved in /home/ that’s your private home listing.
Linux vs Windows, As a everyday consumer, you do not have access to directories of different customers.
Root User
Other than your ordinary account each other consumer account referred to as root is created at the time of set up. The root account is a superuser who can get right of entry to restrained files, set up software program and has administrative privileges.
Linux vs Windows, Whenever you need to put in software, make adjustments to device files or carry out any administrative task on Linux; you want to log in as a root user. Otherwise, for wellknown tasks like gambling track and browsing the net, you can use your normal account.
Service user
Linux is broadly used as a Server Operating System. Services such as Apache, Squid, electronic mail, and many others. Have their personal person service bills.
Linux vs Windows, Having carrier money owed will increase the safety of your laptop. Linux can permit or deny get admission to to numerous resources depending at the service.
Note:
- You will not see carrier bills in Ubuntu Desktop model.
- Regular bills are called wellknown debts in Ubuntu Desktop
In Windows, there are 4 styles of user account kinds.
- Administrator
- Standard
- Child
- Guest
Windows Vs. Linux: File Name Convention
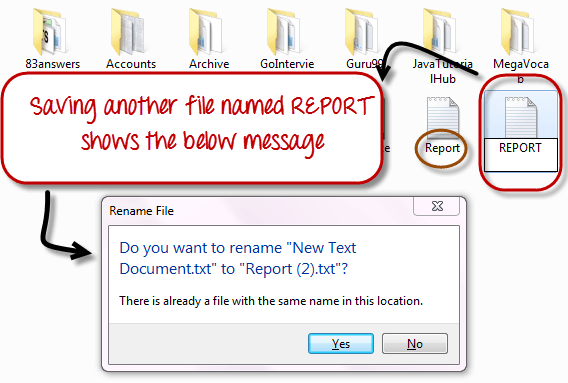
In Windows, you cannot have 2 files with the same name in the same folder. See below
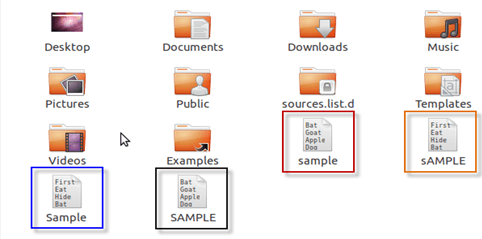
While in Linux, you can have 2 files with the same name in the same directory, provided they use different cases.
Windows Vs. Linux: HOME Directory
For every consumer in Linux, a directory is created as /home/
Consider, a normal person account “Tom”. He can keep his private documents and directories in the directory “/domestic/tom”. He can not save files out of doors his consumer listing and does no longer have get entry to to directories of other customers. For instance, he cannot get admission to listing “/home/jerry” of any other person account”Jerry”.
Linux vs Windows, The idea is similar to C:Documents and Settings in Windows.
When you boot the Linux operating system, your consumer listing (from the above example /home/tom) is the default running directory. Hence the listing “/home/tom is also called the Home listing that is a misnomer.
The working directory can be modified the usage of a few instructions which we will study later.
Windows Vs. Linux: Other Directories
In Windows, System and Program documents are normally stored in C: power. But, in Linux, you would locate the machine and program files in distinct directories. For example, the boot documents are stored in the /boot listing, and program and software program files may be observed under /bin, device files in /dev. Below are vital Linux Directories and a short description of what they contain.
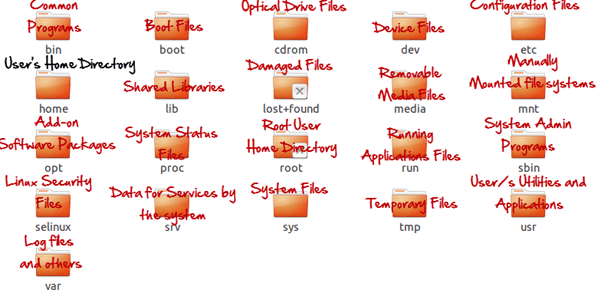
These are most placing variations among Linux and other Operating Systems. There are extra versions you may have a look at whilst switching to Linux and we can discuss them as we pass along in our tutorials.
| Windows | Linux |
|---|---|
| Windows makes use of distinctive records drives like C: D: E to stored files and folders. | Unix/Linux uses a tree like a hierarchical file system. |
| Windows has different drives like C: D: E | There are no drives in Linux |
| Hard drives, CD-ROMs, printers are considered as devices | Peripherals like hard drives, CD-ROMs, printers are also considered files in Linux/Unix |
| There are 4 types of user account types 1) Administrator, 2) Standard, 3) Child, 4) Guest | There are 3 types of user account types 1) Regular, 2) Root and 3) Service Account |
| Administrator user has all administrative privileges of computers. | Root user is the super user and has all administrative privileges. |
| In Windows, you cannot have 2 files with the same name in the same folder | Linux file naming convention is case sensitive. Thus, sample and SAMPLE are 2 different files in Linux/Unix operating system. |
| In windows, My Documents is default home directory. | For every user /home/username directory is created which is called his home directory. |