Befuddled by the contrasts between Intel Core i3, i5, and i7 processors? This is what you need to know in layman’s terms and which CPU to purchase.
The processor is the cerebrum of a PC, yet understanding the distinction between processors requires a great deal of intellectual competence of your own. Sadly, Intel has a confounding naming plan, and the inquiry we get posed regularly is: What’s the distinction between an i3, i5, or i7 processor? Which CPU would it be a good idea for me to purchase?
It’s an ideal opportunity to demystify that. Peruse on to find out about the distinction between an Intel Core i5 and a Core i7, if a Core i3 is any acceptable, and whether you should purchase an Intel Core i9.
The Differences Between Core i7, Core i5, and Core i3

An Intel Core i7 is superior to a Core i5, which thus is superior to a Core i3. The difficulty is realizing what’s in store inside every level. Things go somewhat more profound.
To start with, Core i7 doesn’t mean a seven-center processor! These are simply names to show relative execution.
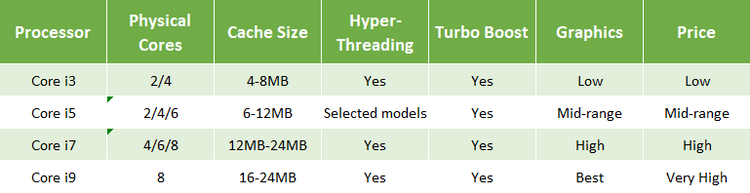
More seasoned Intel Core i3 series had just double center processors, yet later ages have a combination of double and quad-center CPUs.
It’s anything but a comparative story for more established Intel Core i5 CPUs. More seasoned ages of Intel Core i5 processors had a combination of double and quad-center processors, however the later ages regularly highlight a quad-or even hexa-center (six) setup, alongside quicker overclock speeds than the Core i3.
The most recent Intel Core i7 CPU ages incorporate quad-center, hexa-center, and octa-center (eight) arrangements. Once more, the Intel Core i7 CPUs beat their Core i5 partners and are a lot quicker than the passage level Core i3 CPUs.
Quad-centers are normally better compared to double centers and hexa-centers better compared to quad-centers, etc, however it’s anything but consistently precise relying upon the CPU age—more on these distinctions in a second.
Intel discharges “families” of chipsets, called ages. At the hour of composing, Intel has dispatched its eleventh era series, named Rocket Lake. Every family, thusly, has its own line of Core i3, Core i5, and Core i7 series of processors. The most recent CPU ages have another level above Core i7, the Intel Core i9.
The Intel Core i9 series is Intel’s outrageous presentation line. Most Core i9 CPUs are octa-center and accompanied an exceptionally high clock speed, empowering them to perform to an extremely elevated requirement for delayed periods. They may likewise accompany a bigger CPU memory store than their partners, empowering quicker generally speaking execution.
How to Tell Which Intel CPU Generation Is Which?
You can spot which age a processor has a place with by the first digits in quite a while four or five-digit model name. For instance, the Intel Core i7-11700K has a place with the eleventh era.
For quite a while, a helpful dependable guideline for Intel CPU model names was that the other three digits were Intel’s evaluation of how the processor analyzes to others in its own line. For instance, an Intel Core i3-8145U is better than the Core i3-8109U on the grounds that 145 is higher than 109.
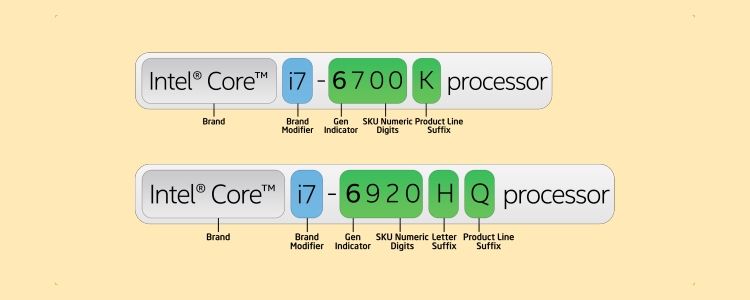
That standard is still set up, yet it’s anything but consistently as simple to follow as it used to be as there are a few other product offering modifiers you can discover in the model number. Nonetheless, “A higher SKU inside in any case indistinguishable processor brands and ages will by and large have more highlights,” according to Intel’s naming show guide.

Moreover, this change is another motivation behind why looking at CPUs across ages utilizing their model number alone is prudent, as Intel changes things.
What Intel’s Model Letter Suffixes Mean: U versus HQ versus H versus K
As should be obvious, the model number will commonly be trailed by one or a mix of the accompanying letters: U, Y, T, Q, H, G, and K. This is what they mean:
- U: Mobile force proficient. The U rating is just for portable processors. These draw less force and are better for battery life.
- Y: Extremely Low Power. Processors intended for gadgets with incredibly low force necessities, like Internet of Things gadgets or other installed equipment.
- T: Power Optimized for work area processors.
- H: High-Performance Mobile. These CPUs are superior models streamlined for portable equipment.
- HK: High-Performance Mobile, yet in addition has an opened CPU which takes into account overclocking.
- HQ: High-Performance Mobile. Streamlined for versatile equipment, with a quad-center processor.
- G: Includes Discrete Graphics. Regularly found on PCs, this implies there is a devoted GPU with the processor.
- G1-G7: The degree of coordinated illustrations execution you can anticipate.
- K: Unlocked. This implies you can overclock the processor over its rating.
- S: Special Edition processors, typically including superior equipment.
Understanding these letters and the numbering framework above will help you understand what a processor offers just by taking a gander at the model number without expecting to peruse the real particulars.
Intel Core i7 versus i5 versus i3: Hyper-Threading
The actual centers to a great extent decide the speed of a processor. However, with how present day CPUs work, you can get a lift in speed with virtual centers, enacted through hyper-stringing.
In layman’s terms, hyper-stringing permits a solitary actual center to go about as two virtual centers, subsequently playing out different assignments all the while without initiating the second actual center (which would require more force from the framework).
On the off chance that the two processors are dynamic and utilizing hyper-stringing, those four virtual centers will figure quicker. Notwithstanding, do take note of that actual centers are quicker than virtual centers. A quad-center CPU will perform obviously superior to a double center CPU with hyper-stringing!
The trouble is that there is no sweeping methodology from Intel in regards to hyper-stringing on its CPUs. For quite a while, just Intel i7 CPUs included hyper-stringing, with a couple of Intel Core i3 CPUs yet no Intel Core i5 CPUs. That circumstance changed with Intel’s tenth Gen CPUs, with some Core i5 processors dispatching with hyper-stringing, yet preceding this, Intel impaired hyper-stringing on a portion of its Intel Core i7 ninth Gen CPUs in light of safety hazards.
So, you’ll need to check the individual CPU for its hyper-stringing potential, as Intel seems to cleave and change with every processor age.
One thing is without a doubt: the quickest Core i9 series upholds hyper-stringing.
Intel Core i7 versus i5 versus i3: Turbo Boost
The entirety of the most recent Intel Core processors presently support Turbo Boost frequencies. Beforehand, Intel Core i3 proprietors were forgotten about in obscurity, compelled to endure with their ordinary CPU speeds. In any case, as of the Intel Core i3-8130U, the CPU maker started adding higher recurrence modes to the passage level CPU series.
Obviously, Core i5, Core i7, and Core i9 CPUs all element Turbo Boost, as well.
Super Boost is Intel’s exclusive innovation to keenly build a processor’s clock speed if the application requests it. Along these lines, for instance, in the event that you are playing a game and your framework requires some additional torque, Turbo Boost will kick in to redress.
Super Boost is helpful for the individuals who run asset concentrated programming like video editors or computer games, however it doesn’t have quite a bit of an impact in case you’re simply perusing the web and utilizing Microsoft Office.
Intel Core i7 versus i5 versus i3: Cache Size
Aside from Hyper-Threading and Turbo Boost, the one other significant contrast in the Core setup is Cache Size. The reserve is the processor’s own memory and behaves like its private RAM. Moving up to a more current CPU with a bigger memory store is one of the updates that will profit your PC the most.
Very much like with RAM, more reserve size is better. So if the processor is performing one undertaking over and over, it will keep that assignment in its reserve. On the off chance that a processor can store more assignments in its private memory, it can do them quicker in the event that they come up once more.
The most recent ages of Core i3 CPUs normally accompany between 4-8MB of Intel Smart Cache memory. The Core i5 series has somewhere in the range of 6MB and 12MB of Intel Smart Cache memory, and the Core i7 series has somewhere in the range of 12MB and 24MB of reserve. The Intel Core i9 series beat the rundown, with every CPU accompanying somewhere in the range of 16MB and 24MB Intel Smart Cache memory.
Intel Graphics: Xe, HD, UHD, Iris, Iris Pro, or Plus
Since the time designs were incorporated on the processor chip, coordinated illustrations have become a significant choice point in purchasing CPUs. In any case, similarly as with all the other things, Intel has made the framework somewhat aggravating.
- Intel Graphics Technology is the umbrella term covering all Intel incorporated designs. Inside that, there are various ages of Intel coordinated designs innovation, confusingly alluded to by both series names and generational names. As yet following?
- Intel HD Graphics was first presented in 2010 as the primary series under this umbrella yet is really Gen5 (fifth era) as far as improvement.
- Intel Iris Graphics and Intel Iris Pro Graphics were presented in 2013 and are Gen7 coordinated designs units. The Iris Pro Graphics units were quite huge information at the time as they incorporated DRAM into the module, giving the designs execution an additional lift.
- Intel UHD Graphics dispatched with Intel’s tenth Generation portable CPUs and is just accessible on certain PC model processors.
Intel Xe (known as Gen12 coordinated realistic) was an enormous advance advances for incorporated illustrations, utilizing another design to convey a lot higher incorporated illustrations execution than past ages. Adding to the disarray, a portion of the Intel UHD Graphics models use Intel Xe engineering, further muddying the water.
The best guidance for how to decipher these? Simply don’t. All things considered, depend on Intel’s naming framework. In the event that the processor’s model finishes with HK, you realize it’s a model with high illustrations execution and an opened CPU. On the off chance that it’s anything but a G, that implies there is a devoted GPU, not one of Intel’s chips.
Picking Between Intel Cores i3 versus i5 versus i7 versus i9
By and large talking, here’s who every processor type is best for:
- Intel Core i3: Basic clients. Financial decision. Useful for perusing the web, utilizing Microsoft Office, settling on video decisions, and interpersonal interaction. Not for gamers or experts.
- Intel Core i5: Intermediate clients. The individuals who need a harmony among execution and cost. Useful for gaming on the off chance that you purchase a G processor or a Q processor with a committed designs processor.
- Intel Core i7: Power clients. You perform various tasks with a few windows open simultaneously, you run applications that require a ton of drive, and you disdain trusting that anything will stack.
- Intel Core i9: The outrageous presentation level is promoted for those that request the best and quickest exhibition in each space of their machine.
How Might You Choose Between Intel Core CPUs?
This article gives an essential manual for anybody hoping to purchase another Intel processor yet is befuddled between Core i3, i5, and i7. However, even subsequent to seeing this, when it’s an ideal opportunity to settle on a choice, you may have to pick between two processors from various ages since they’re valued something very similar.
At the point when you’re contrasting, my best tip is to go to CPU Boss, where you can analyze the two processors and get a nitty gritty examination, just as evaluations. On the off chance that you don’t comprehend the language, simply go with the rating and the essential exhortation. Regardless of whether you comprehend CPU language, CPU Boss has every one of the subtleties you’ll require.
A great many people Don’t Need Intel Core i9
Albeit the ultra-execution models in the Intel Core i9 territory appear to be unfathomably energizing (and they will be!), they are a piece over the top excess for most clients. Intel markets those at supportive of gamers, fashioners, content makers, designers, and that’s just the beginning, and for a valid justification. More often than not, a top-level Intel Core i7 CPU will do the work and save you a reasonable whack of money simultaneously.
Be that as it may, each to their own, obviously, and on the off chance that you can manage the cost of an Intel Core i9 CPU for your gaming rig, get it and appreciate the unfathomable experience.