Dual Boot Linux and Mac OS The Mac is an first-rate platform for going for walks now not best the Mac OS, which includes macOS Sierra however additionally Windows and Linux. The MacBook Pro is a famous platform for walking Linux.
Under the hood, Mac’s hardware is remarkably much like maximum of the elements utilized in present day PCs. You’ll discover the equal processor households, graphics engines, networking chips, and a first-rate deal extra
Install and Dual Boot Linux and Mac OS Running Windows on a Mac
When Apple modified from PowerPC structure to Intel, many puzzled if the Intel Macs could run Windows. Turns out, the handiest real stumbling block become getting Windows to run on an EFI-based motherboard in place of the then a whole lot greater commonplace BIOS-primarily based designs.
Apple even lent a hand to the effort by means of releasing Boot Camp, a software that blanketed Windows drivers for all the hardware in the Mac, the capability to assist a user in putting in the Mac for twin booting between the Mac OS and Windows, and an assistant for partitioning and formatting a drive for use by means of the Windows OS.
Running Linux on a Mac Install and Dual Boot Linux and Mac OS (Dual Boot Linux and Mac)
If you could run Windows on a Mac, you should be able to run pretty much any OS that is designed for the Intel structure, proper? In general, this is real, despite the fact that, as with many things, the satan is in the details. Many Linux distributions can run well on a Mac, although there can be challenges to installing and configuring the OS.
Install and Dual Boot Linux and Mac OS Level of Difficulty (Dual Boot Linux and Mac)
Dual Boot Linux and Mac, This venture is for superior users who’ve the time to paintings thru troubles that can increase alongside the way and are willing to reinstall the Mac OS and their data if issues arise during the process.
There may not be any huge troubles, however the capability exists. Be prepared, have a modern-day backup, and read through the complete system before installing Ubuntu.
Installation and Drivers

The problems that arise whilst getting a Linux distribution operating on a Mac usually revolve round hassle regions: getting an installer to work correctly with the Mac and finding and installing all of the wished drivers so the important components of the Mac work. This can include locating the drivers required for Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, in addition to the drivers needed for the portraits gadget your Mac uses.
It’s a disgrace Apple doesn’t offer time-honored drivers that might be used with Linux, along with a basic installer and assistant as it has achieved with Windows, however till that occurs, you need to address the installation and configuration problems your self.
This manual assist you to get a fave Linux distribution operating on a Mac and introduce you to assets that assist you to tune down the drivers you need or solve set up troubles you may encounter.
Ubuntu
There are many Linux distributions you may pick out from for this mission consisting of Debian, MATE, primary OS, Arch Linux, OpenSUSE, Ubuntu, and Mint. This manual uses Ubuntu, specially due to the active forums and support to be had from the Ubuntu network and the coverage of Ubuntu furnished online.
Why Install Ubuntu on Your Mac?
Dual Boot Linux and Mac, There are a ton of reasons to want Ubuntu or your favorite Linux distribution going for walks for your Mac. You may need to expand your era chops, find out about a specific OS, or have one or extra unique apps you need to run. You can be a Linux developer and realise that the Mac is the great platform to use, or you may truly need to strive out Ubuntu.
No depend the cause, this manual facilitates you put in Ubuntu on your Mac and allow your Mac to without difficulty twin boot among Ubuntu and macOS. This approach for dual booting can without problems be accelerated to triple booting or extra.
What You Need
You need several things before you can start:
- A current backup. Use Carbon Copy Cloner or a comparable application to clone an outside bootable power that consists of a replica of the Recovery HD extent. After you have got a working clone, disconnect it from your Mac to ensure that the clone backup isn’t always by chance erased in the course of the Ubuntu set up.
- A Mac with 2GB of RAM and a 2 GHz dual-middle processor. These are the bare minimums; greater RAM and quicker processor speeds or extra processor cores are useful. The set up defined right here is on a 2014 27-inch Retina iMac going for walks macOS Sierra, however the method should work for any Mac released after 2011. If you plan to use an older Mac, you must nevertheless be able to set up Ubuntu, but you need to take note of how the boot technique works for older hardware. If you have problems getting your older Mac to paintings with Ubuntu, stop through the Ubuntu boards and look for set up guides for your Mac version.
- A 2GB or large USB flash force. The flash pressure is used as a bootable Ubuntu installer that incorporates now not most effective the simple installer however additionally a live version of Ubuntu that you can run immediately from the USB flash power without editing some thing to your Mac. This is a splendid manner to check whether or not your Mac and Ubuntu can get along.
- A USB keyboard and mouse. You want a USB-based totally keyboard and mouse because it’s distinctly probably that the Ubuntu Bluetooth drivers will need to be installed or up to date before a wireless keyboard or mouse can work.
- 25GB loose force space. This is the minimum length encouraged for the laptop model of Ubuntu; greater area to paintings with may be a advantage.
- Ubuntu 16.04.1 LTS. This is the modern solid model of Ubuntu that turned into available while we started out this assignment. Later versions must paintings as nicely. Check the discharge notes for any precise adjustments which can affect set up or use for your Mac.
- A current backup. Use Carbon Copy Cloner or a similar application to clone an outside bootable drive that consists of a copy of the Recovery HD extent. After you have a operating clone, disconnect it out of your Mac to ensure that the clone backup isn’t accidentally erased at some point of the Ubuntu set up.
- A Mac with 2GB of RAM and a 2 GHz twin-center processor. These are the bare minimums; more RAM and faster processor speeds or additional processor cores are helpful. The set up described right here is on a 2014 27-inch Retina iMac strolling macOS Sierra, however the procedure ought to work for any Mac launched after 2011. If you plan to use an older Mac, you need to still be able to set up Ubuntu, however you want to be aware of how the boot process works for older hardware. If you have issues getting your older Mac to paintings with Ubuntu, prevent with the aid of the Ubuntu boards and look for install publications in your Mac version.
- A 2GB or larger USB flash pressure. The flash power is used as a bootable Ubuntu installer that consists of no longer handiest the primary installer but also a live model of Ubuntu that you can run directly from the USB flash power without editing some thing for your Mac. This is a notable manner to test whether or not your Mac and Ubuntu can get alongside.
- A USB keyboard and mouse. You need a USB-based keyboard and mouse as it’s surprisingly in all likelihood that the Ubuntu Bluetooth drivers will need to be established or up to date before a wi-fi keyboard or mouse can work.
- 25GB unfastened power area. This is the minimum length recommended for the desktop model of Ubuntu; more area to work with can be a advantage.
- Ubuntu sixteen.04.1 LTS. This is the current solid model of Ubuntu that become available whilst we started this undertaking. Later variations have to paintings as properly. Check the discharge notes for any specific changes which could have an effect on set up or use on your Mac.
Create a Live Bootable USB Ubuntu Installer for Mac OS
The first task in putting in and configuring Ubuntu for your Mac is to create a live bootable USB flash pressure that consists of the Ubuntu Desktop OS. Use this flash power to no longer best deploy Ubuntu but additionally to confirm that Ubuntu can run for your Mac. You should be able to boot Ubuntu immediately from the USB stick while not having to carry out an deploy. This helps you to test basic operations before you commit to altering your Mac’s configuration to deal with Ubuntu.
Preparing the USB Flash Drive
One of the primary obstacles you could encounter is how the flash force must be formatted. Many parents mistakenly trust the flash drive needs to be in a bootable FAT layout, requiring the partition type to be Master Boot Record, and the format kind to be MS-DOS (FAT). While this could be real of installations on PCs, your Mac is seeking out GUID partition types for booting, so the USB flash pressure need to be formatted for use on the Mac
Warning: The following process completely erases any data you have on the USB flash drive.
- Ert the USB flash pressure and release Disk Utility, that’s positioned at /Applications/Utilities/.
- Locate the flash pressure in Disk Utility’s sidebar. Select the actual flash pressure and no longer the formatted extent which could appear simply under the flash drive’s producer call.
- Click Erase in the Disk Utility toolbar.
- Set the Erase options as follows: Name: UBUNTU, Format: MS-DOS (FAT), Scheme: GUID Partition Map.
- Click Erase.
- When the process is whole, click Done.
- Before you depart Disk Utility, make a notice of the flash pressure’s tool call. Make certain the flash force named UBUNTU is chosen inside the sidebar, and search for the access labeled Device in the important panel. You need to see the tool call, which includes disk2s2, or comparable. Write down the device name. You need it later.
- Quit Disk Utility.
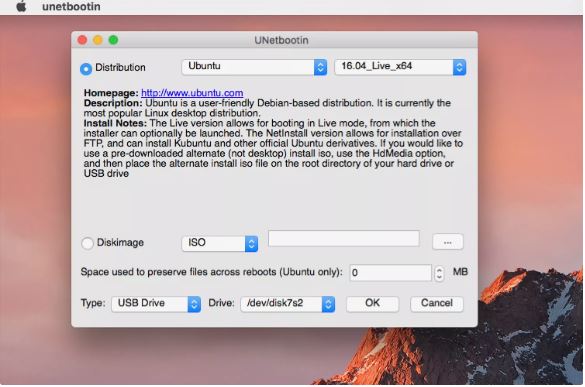
UNetbootin Utility
Dual Boot Linux and Mac, The UNetbootin application creates the stay Ubuntu installer at the USB flash force. UNetbootin downloads the Ubuntu ISO, converts it to an image format the Mac can use, creates the boot chain wished by way of the installer for the Mac OS, and then copies it to the USB flash power.
- UNetbootin can be downloaded from the UNetbootin GitHub site. Select the Mac OS X model even if you’re the use of macOS Sierra. The application downloads as a disk image, with the name unetbootin-mac-625.Dmg. The actual variety inside the report name can also alternate as more recent variations are launched.
- Locate the downloaded UNetbootin disk image. It might be in your Downloads folder.
- Double-click the .Dmg file to mount the picture in your Mac’s computer. The UNetbootin picture opens. You don’t want to transport the app in your Applications folder, although you can if you want. The app works simply best from inside the disk picture.
- Launch UNetbootin by means of right-clicking at the unetbootin app and choosing Open from the popup menu. Use this technique to release the app due to the fact the developer isn’t always a registered Apple developer, and your Mac’s safety settings can also save you the app from launching. This method of launching the app bypasses the simple protection settings without having to enter the System Preferences to trade them.
- Your Mac’s safety device will nonetheless warn you approximately the developer of the app being unrecognized and ask in case you really need to run the app. Click Open.
- A conversation box open, pronouncing osascript desires to make adjustments. Enter your administrator password and click OK.
- The UNetbootin window opens. UNetbootin supports developing the live USB installer for Linux using an ISO report you formerly downloaded, or it could download the Linux distribution for you. Do not pick the ISO option. UNetbootin is currently not able to create a Mac-compatible bootable USB force the usage of a Linux ISO you download because the source. It can, but, nicely create the bootable USB force when it downloads the Linux documents from inside the app.
- Make sure Distribution is selected and then use the Select Distribution drop-down menu to pick out the Linux distribution you need to install at the USB flash pressure. For this venture, pick Ubuntu.
- Use the Select Version drop-down menu to choose sixteen.04_Live_x64, the version this is well matched with sixty four-bit structure. Some early Intel Macs used 32-bit structure, and you can need to pick the sixteen.04_Live model rather. If you’re adventurous, choose the Daily_Live or Daily_Live_x64 variations, which have the maximum cutting-edge beta model of Ubuntu. This can be helpful when you have issues with the live USB going for walks effectively on your Mac or with drivers such as Wi-Fi, Display, or Bluetooth not working.
- The UNetbootin app need to now list the kind (USB Drive) and Drive name that the Ubuntu live distribution might be copied to. The Type menu ought to be populated with USB Drive, and the Drive should healthy as much as the device call you made a notice of earlier when you were formatting the USB flash drive. After you verify that UNetbootin has the right distribution, version, and USB drive decided on, click the OK button.
- UNetbootin downloads the chosen Linux distribution, creates the live Linux set up files, creates the bootloader, and copies them in your USB flash drive.
- When UNetbootin finishes, you could see the subsequent caution: The created USB tool will not boot off a Mac. Insert it right into a PC, and pick out the USB boot choice in the BIOS boot menu. You can ignore this warning so long as you used the Distribution option and now not the ISO choice whilst growing the bootable USB pressure.
- Click the Exit button.
The live USB flash drive containing Ubuntu has been created and is ready to try out on your Mac.
Creating a Ubuntu Partition on Your Mac
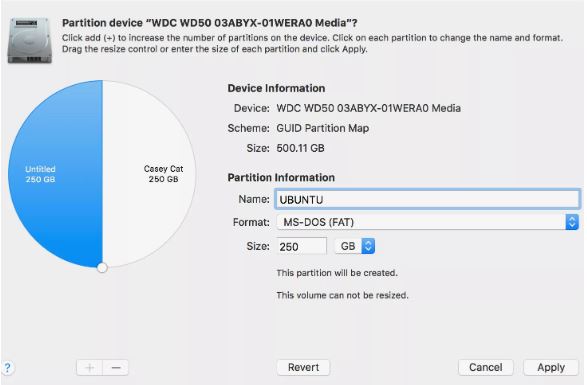
If you propose on permanently putting in Ubuntu in your Mac while retaining the Mac OS, you need to create one or greater volumes specially for housing the Ubuntu OS.
The method is simple. You use Disk Utility to partition an current volume, which includes your Mac’s startup pressure, to make room for a 2d volume. You may also use a whole power other than your startup power, to residence Ubuntu, or you may create some other partition on a nonstartup drive. There are lots of alternatives.
Just to feature some other alternative, you may also set up Ubuntu on an external force connected through USB or Thunderbolt.
Ubuntu Partitioning Requirements
Dual Boot Linux and Mac, You might also have heard that Linux OSes need more than one walls to run at their excellent; one partition for disk swap space, every other for the OS, and a 3rd for personal records.
While Ubuntu can use more than one walls, it is also able to being established in a single partition, that’s the technique used here. You can always add a swap partition later from inside Ubuntu.\
Why Create Just One Partition Now?
You’re going to apply the disk partitioning software covered with Ubuntu to create the wished storage space. What you want the Mac’s Disk Utility to do is define that area, so it’s smooth to pick out and use while putting in Ubuntu. Think of it this manner: when you get to the point inside the Ubuntu set up wherein the force area is assigned, you don’t need to pick the existing Mac OS pressure accidentally, or any of the Mac OS facts drives you operate. Creating the space erases any facts on the selected quantity.
Instead, you create a extent with an smooth-to-discover call, format, and size that stands proud when it comes time to pick out a volume for the Ubuntu installation.
Use Disk Utility to Create the Ubuntu Install Target
If you’ll use an present partition, take a look at those two publications for resizing and partitioning:
- Disk Utility: How to Resize a Mac Volume (OS X El Capitan or Later)
- Partition a Drive with OS X El Capitan’s Disk Utility
Warnings:Partitioning, resizing, and formatting any force can bring about facts loss. Make sure you’ve got a contemporary backup of any facts on the selected drives concerned. Tips:If you’re using a Fusion pressure, the Mac OS imposes a restriction of partitions on the Fusion extent. If you’ve already created a Windows Boot Camp partition, you might not be capable of add a Ubuntu partition as well. Consider the use of an outside power with Ubuntu as an alternative.
If you propose on the usage of an entire power for Ubuntu, use the formatting guide:
Format a Mac’s Drive Using Disk Utility (OS X El Capitan or later)
No count number which of the guides you operate, the partition scheme need to be GUID Partitioning Map, and the layout can be MS-DOS (FAT) or ExFat. The format will exchange when you installation Ubuntu. Its purpose is handiest to make it easy to discover which disk and partition you use for Ubuntu later in the deploy process.
Give the volume a meaningful call, along with UBUNTU and make a be aware of the partition size you’re making. Both portions of records are useful in identifying the quantity later all through the Ubuntu install.
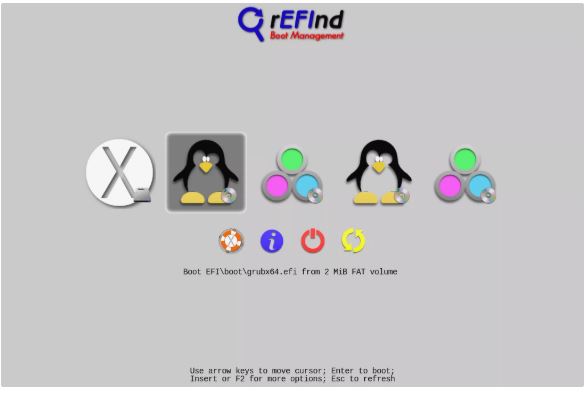
Using rEFInd as Your Dual-Boot Manager
Dual Boot Linux and Mac, So a long way, you’ve worked on getting your Mac equipped to receive Ubuntu and prepared a bootable installer you may use for the method. Now you want to take steps as a way to dual boot your Mac into the Mac OS in addition to the brand new Ubuntu OS.
Boot Managers
Your Mac already comes ready with a boot manager that helps you to pick among multiple Mac or Window OSes that can be established for your Mac. You can invoke the boot manager at startup by way of keeping down the Option key, inclusive of is defined within the Using the OS X Recovery Disk Assistant guide.
Ubuntu comes with its personal boot manager, known as GRUB (GRand Unified Boot Loader). You’ll use GRUB shortly when you run through the set up process.
Both of the boot managers to be had to use can handle the twin-booting process; they can even deal with greater OSes than simply two, but the Mac’s boot supervisor received’t understand the Ubuntu OS without a piece of fiddling, and the GRUB boot manager simply especially smooth to use.
Instead, make use of a third-birthday party boot supervisor referred to as rEFInd. REFInd can manage all the Mac’s booting wishes, together with letting you pick out the Mac OS, Ubuntu, or Windows, if you occur to have it established.
Installing rEFInd
REFInd is easy to put in; a easy Terminal command is all that’s wanted if you’re the use of OS X Yosemite or earlier. OS X El Capitan and later has an additional safety layer known as SIP (System Integrity Protection). In a nutshell, SIP prevents everyday users, along with administrators, from changing machine files, such as desire files and folders the Mac OS uses for itself.
As a boot manager, rEFInd desires to put in itself within areas blanketed by means of SIP, so in case you’re the usage of OS X El Capitan or later, you may need to disable the SIP machine before intending.
Disabling SIP
- Use the commands inside the Using the OS X Recovery Disk Assistant manual to restart your Mac the usage of the Recovery HD.
- Select Utilities > Terminal from the menus.
- In the Terminal window that opens, input the subsequent: csrutil disable
- Press Enter or Return.
- Restart your Mac.
- Once you’ve got the Mac laptop lower back, release Safari and down load rEFInd from SourceForge at rEFInd beta, an EFI boot supervisor application. When the download completes, you could find it in a folder named refind-bin-0.10.4. (The number on the cease of the folder call may additionally alternate as new variations are released.) Open the refind-bin-0.10.4 folder.
- Launch Terminal, placed at /Applications/Utilities/.
- Arrange the Terminal window and the refind-bin-zero.10.4 Finder window in order that each may be seen.
- Drag the report named refind-installation from the refind-bin-0.10.4 folder to the Terminal window.
- In the Terminal window, press Enter or Return.
- REFInd is hooked up on your Mac.
Optional but recommended:
- Turn SIP lower back on with the aid of getting into the subsequent in Terminal: csrutil enable.
- Press Enter or Return.
- Close Terminal.
- Shut down your Mac. (Do not restart. Use the Shut Down command.)
Using the Live USB Drive to Try Out Ubuntu on Your Mac
The stay USB for Ubuntu you created in advance can be used for permanently installing Ubuntu for your Mac and for attempting out Ubuntu with out putting in the OS. You can leap to an set up, but try Ubuntu first. The principal reason is that you can discover troubles earlier than committing to a full install.
Some of the problems you can discover include the install of stay USB now not operating along with your Mac portraits card. This is one of the more not unusual issues Mac customers face while installing Linux. You may additionally discover that your Wi-Fi or Bluetooth is not working. Most of those problems can be corrected after the install, however understanding approximately them in advance of time helps you to do some studies out of your acquainted Mac surroundings. You can song down the troubles and possibly acquire wanted drivers or at the least know in which to get them earlier than the installation.
Dual Boot Linux ( Ubuntu ) and Mac
Trying Out Ubuntu on Your Mac
Before you try booting to the live USB drive you created, there’s a bit of preparation to perform.
- Ke sure the Live USB flash force is attached directly to certainly one of your Mac’s USB or Thunderbolt ports. Do no longer use a USB hub, because it’s commonplace for the Live USB flash pressure to fail to show up whilst related through a hub.
- Make sure you have got a USB keyboard and USB mouse related to your Mac. Another of the commonplace problems is missing Bluetooth drivers, which prevent your wireless keyboard and mouse from being used.
- If feasible, connect your Mac to your property network via a stressed Ethernet port. This is for the equal purpose because the wi-fi keyboard or mouse. The Wi-Fi drivers can also need to be updated or brought to get your wireless community operating.
If you’re ready, let’s give it the boot.
- Shut down or restart your Mac. If you mounted rEFInd, the boot manager automatically appears. If you chose no longer to apply rEFInd, then as soon as your Mac begins in addition up, keep down the Option key. Keep retaining it down until you see the Mac’s boot supervisor show a list of to be had gadgets you may start up from.
- Use the arrow keys to choose either the Boot EFIboot… Entry (rEFInd) or the EFI Drive access (Mac boot supervisor) from the listing. If you don’t see an EFI Drive or Boot EFIboot… In the list, close down and make sure the stay USB flash force is hooked up without delay for your Mac. You may also need to do away with all peripherals out of your Mac, besides the mouse, keyboard, USB stay flash force, and wired Ethernet connection.
- After you select the Boot EFIboot… Or EFI Drive icon, press Enter or Return on the keyboard.
- Your Mac will boot using the stay USB flash pressure and present the GRUB 2 boot supervisor. You’ll see a fundamental textual content show with as a minimum 4 entries:
- Try Ubuntu without installing it.
- Install Ubuntu.
- OEM install (for manufacturers).
- Check disc for defects.
- Use the arrow keys to pick Try Ubuntu with out installing and then press Enter or Return.
- The display is going darkish for a brief time after which shows a Ubuntu splash display screen, accompanied by the Ubuntu computer. The total time for this need to be 30 seconds to three minutes. If you should wait longer than 5 mins, there’s possibly a snap shots trouble. If your display stays black, you in no way depart the Ubuntu splash display, or the display becomes unreadable, you probably have a pics motive force trouble. You can restore this by using editing the Ubuntu boot loader command as mentioned beneath.
Modifying the GRUB Boot Loader Command
- Shut down your Mac by means of urgent and retaining the Power button.
- After the Mac shuts down, restart and return to the GRUB boot loader display screen the usage of the instructions above.
- Select Try Ubuntu with out putting in but do now not press the Enter or Return key. Instead, press the ‘e’ key to enter an editor that lets in you to make modifications to the boot loader instructions.
- The editor consists of some strains of textual content. You need to alter the line that reads:
linux/casper/vmlinuz.efi file=/cdrom/preseed/Ubuntu.seed boot=casper quiet splash ---- Between the words ‘splash’ and ‘—‘ insert the following:nomodeset
- The line should end up looking like this:
linux /casper/vmlinuz.efi file=/cdrom/preseed/Ubuntu.seed boot=casper quiet splash nomodeset ---- To make the edit, use the arrow keys to transport the cursor to the area just after the word splash after which kind nomodeset. There should be a space between splash and nomodeset and a area between nomodeset and —.
- Press F10 to boot with the new settings.
Note:The adjustments you simply made aren’t saved. They’re used simply this one time. Should you need to apply the Try Ubuntu without putting in alternative inside the destiny, you’ll want to edit the road over again.
Adding nomodeset is the maximum not unusual approach of correcting a portraits problem when installing, however it is no longer the handiest one. If you continue to have show problems, you may attempt the following:
Determine the make of the graphics card your Mac makes use of. You can try this by way of deciding on About This Mac from the Apple menu. Look for the text Graphics, make a word of the pix getting used, and then use one of the following values in place of nomodeset:
nvidia.modeset=0
radeon.modeset=0
intel.modeset=0
If you’re nonetheless having issues with the show, take a look at the Ubuntu boards for troubles along with your specific Mac model.
Now which you have a stay version of Ubuntu walking for your Mac, check to ensure your Wi-Fi network is operating, in addition to Bluetooth, if wanted.
Installing Ubuntu on Your Mac
Dual Boot Linux and Mac, By now, you’ve got a running stay USB flash drive that contains the Ubuntu installer, your Mac configured with a partition geared up for use for putting in Ubuntu, and an itchy mouse finger simply waiting to click at the Install Ubuntu icon you spot at the live Ubuntu computer.
Install Ubuntu
- If you are ready, double-click on the Install Ubuntu icon.
- Select the language to use after which click on Continue.
- Allow the installer to download updates as needed, for each the Ubuntu OS as well as drivers you may need. Place a take a look at mark within the Download Updates while putting in Ubuntu take a look at field and in the Install 1/3-celebration software for images and Wi-Fi hardware, Flash, MP3, and different media take a look at container. Click the Continue button.
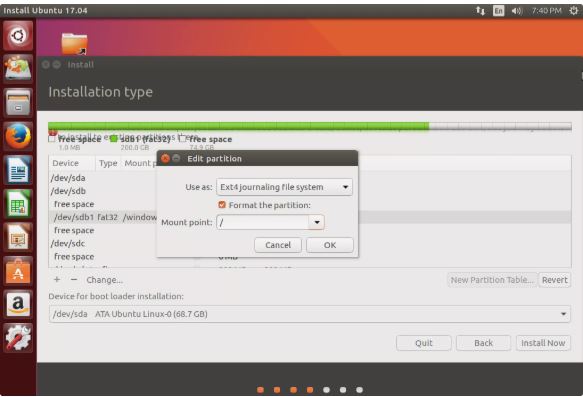
- Ubuntu offers a number of set up kinds. To deploy Ubuntu on a specific partition, choose Something Else from the list and then click on Continue.
- The installer offers a list of garage devices connected in your Mac. You need to locate the quantity you created the use of the Mac’s Disk Utility. Because the device names are extraordinary, use the size and format of the volume you created. After you discover the appropriate quantity, use the mouse or arrow keys to spotlight the partition and then click on the Change button.
- Note: Ubuntu shows the partition size in megabytes (MB), even as the Mac shows the scale as gigabytes (GB). 1GB equals 1000MB.
- Use the Use as drop-down menu to pick out the report gadget to apply, preferably the ext4 journaling report system.
- Use the Mount Point drop-down menu to select the forward scale back (/), that is referred to as the basis. Click the OK button.
- You may be warned that deciding on a new partition length needs to be written to the disk. Click the Continue button.
- With the partition you just modified selected, click the Install Now button.
- You can be warned that you did now not define any partition for use for swap area, however you could upload switch space later. Click the Continue button.
- You are notified that the modifications you made are approximately to be devoted to the disk. Click the Continue button.
- Select a time quarter from the map or enter a major metropolis inside the discipline. Click Continue.
- Choose the keyboard format and click Continue.
- Set up your Ubuntu consumer account through getting into your name, a name for the computer, a username, and a password. Click Continue.
- The set up technique will start, with a status bar showing the progress. When the installation completes, you may click the Restart button.
You now have a operating version of Ubuntu established on your Mac.
After the restart completes, you can be aware that the rEFInd boot supervisor is now running and displays the Mac OS, the Recovery HD, and the Ubuntu OS. You can click on on any of the OS icons to select the working system you need to use.
Click the Ubuntu icon.
If after restarting you’ve got problems, which includes missing or nonfunctional gadgets (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, printers, or scanners), test with the Ubuntu community for tips approximately getting all of your hardware working. (Dual Boot Linux and Mac)