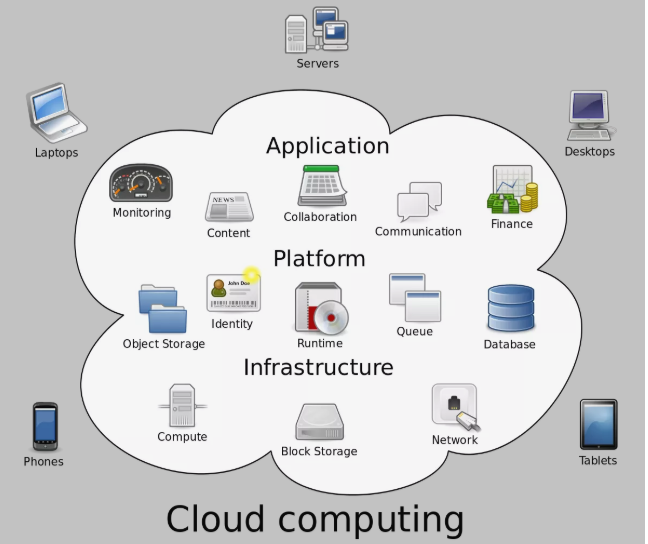
Cloud computing includes hardware and software sources made to be had at the internet as managed external services. These offerings rely on advanced software program programs and high-cease networks of server computers.
Types of Cloud Computing
Service providers create cloud computing structures to serve not unusual business or research needs. Examples of cloud computing offerings encompass:
Virtual IT (facts generation): Configure and install far flung external servers as extensions to a corporation’s nearby IT community. Software: Use industrial software packages, or develop and remotely host custom-constructed packages, Network garage: Network storage information data across the net to a provider without needing to realize the physical region of storage. Cloud computing systems all normally are designed to help big numbers of clients and surges in call for.
Software-As-A-Service Models
Cloud services using a software program-as-a-provider version, or SaaS, provide fully useful applications to cease customers even though the programs won’t be resident on their nearby computer systems.
Email providers like Gmail and Outlook.Com are SaaS applications, in addition to pretty much any computer program that runs inside a browser. As such, SaaS is maximum familiar to domestic clients.
Platform-as-a-Service Models
A SaaS answer sits atop a platform. Vendors that provide platform-as-a-carrier portfolios generally face company clients. PaaS products include virtual servers, running environments, database environments, and another middleware component that sits among the hardware and the patron-facing application.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service Models
Platforms, in turn, sit upon infrastructure. Infrastructure-as-a-provider answers normally get to the extent of ‘naked metal’ — the physical servers, networking additives, and tool storage essential to make platforms (and, subsequently, services) useful. IaaS is popular with corporate clients, with tradeoffs among pace, cost, and privacy that each vendor balances in distinct ways.
Examples of Cloud Computing Services
Many exclusive vendors provide numerous forms of cloud-computing offerings:
Amazon EC2 — Virtual IT Google App Engine — Application website hosting Google Apps and Microsoft Office Online — SaaS Apple iCloud — Network storage DigitalOcean — Servers (Iaas/PaaS) Some vendors provide cloud computing services free of charge, at the same time as others require a paid subscription.
How Cloud Computing Works
A cloud computing gadget continues its essential information on net servers as opposed to distributing copies of facts files to individual client gadgets. Video-sharing cloud offerings like Netflix, for example, flow information across the net to a player software at the viewing device in preference to sending customers DVD or BluRay bodily discs.
Clients must be connected to the net in order to use cloud services. Some video video games at the Xbox Live service, for example, can best be acquired online (not on bodily disc), while a few others additionally can’t be performed without being related.
Some industry observers assume cloud computing to maintain growing in popularity in coming years. The Chromebook is one instance of ways all non-public computers may evolve within the destiny under this trend — devices with minimal neighborhood garage area and few local packages except the web browser (through which online applications and offerings are reached).
Cloud Computing Pros and Cons
As with any disruptive new era, cloud computing gives strengths and weaknesses that builders and consumers alike should cautiously evaluate.
Service carriers are responsible for installing and keeping middle technology inside the cloud. Some commercial enterprise customers decide upon this model as it limits their personal burden of having to preserve infrastructure. Conversely, these customers surrender management manipulate over the system, counting on the provider to supply the needed reliability and overall performance degrees.
Likewise, home customers come to be especially dependent on their internet company within the cloud computing version: Temporary outages and slower-velocity broadband which are a minor nuisance nowadays end up a significant hassle in a fully cloud-based totally international. On the opposite hand — proponents of cloud technology argue — such an evolution would probable pressure net carriers to maintain enhancing the exceptional of their service to live competitive.
Cloud computing systems are generally designed to intently music all system resources. This, in flip, permits carriers to rate clients fees proportional to their network, storage, and processing utilization. Some customers pick this metered billing approach to saving cash, at the same time as others select a flat-price subscription to ensure predictable monthly or yearly costs.
Using a cloud computing surroundings generally requires you to ship facts over the internet and store it on a supplier-controlled gadget. The privateness and safety dangers associated with this model need to be weighed against the benefits in addition to the options.
The Bottom Line for Consumers
The common non-IT purchaser advantages from SaaS/PaaS/IaaS technologies due to the lower cost, quicker deployment time, and extended flexibility that those solutions offer. Although a few people opt to own the license to a bit of unchanging software program, others are content to embody subscription-based totally software that calls for internet connectivity.