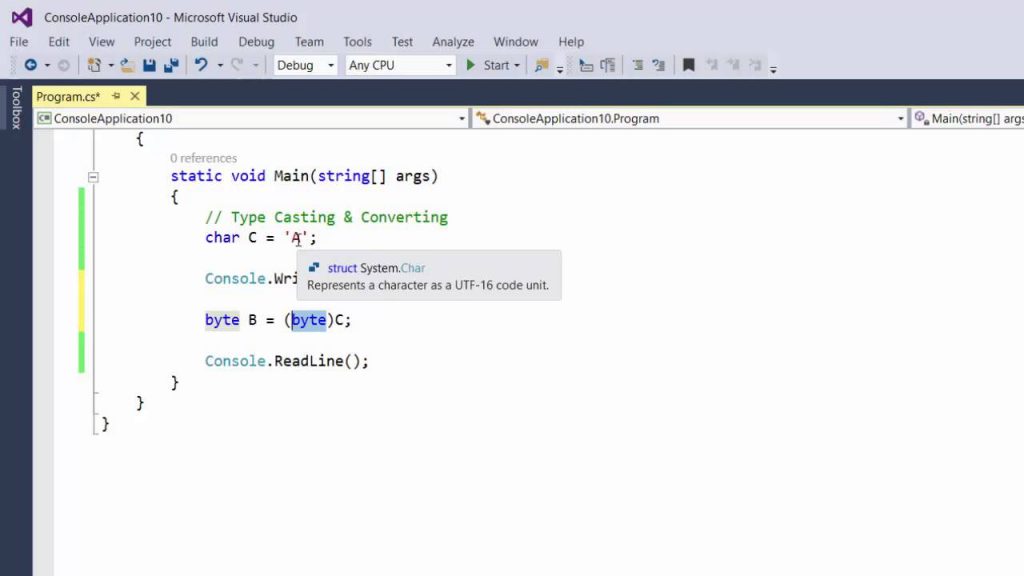
Type conversion, is changing one form of data to every other kind. It is likewise referred to as Type Casting. In C#, kind casting has forms
- Implicit kind conversion − These conversions are accomplished by using C# in a type-secure way. For instance, are conversions from smaller to larger imperative sorts and conversions from derived training to base instructions.
- Explicit type conversion − These conversions are carried out explicitly by using users the usage of the pre-described features. Explicit conversions require a forged operator.
The following instance indicates an specific kind conversion
using System;
namespace TypeConversionApplication {
class ExplicitConversion {
static void Main(string[] args) {
double d = 5673.74;
int i;
// cast double to int.
i = (int)d;
Console.WriteLine(i);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}When the above code is compiled and finished, it produces the following end result
5673
C# Type Conversion Methods
C# provides the subsequent integrated kind conversion techniques
ToBoolean
- Converts a type to a Boolean fee, in which feasible.
ToByte
- Converts a type to a byte.
ToChar
- Converts a type to a single Unicode man or woman, in which feasible.
ToDateTime
- Converts a type (integer or string kind) to date-time structures.
ToDecimal
- Converts a floating factor or integer type to a decimal type.
ToDouble
- Converts a type to a double type.
ToInt16
- Converts a type to a sixteen-bit integer.
ToInt32
- Converts a type to a 32-bit integer.
ToInt64
- Converts a type to a 64-bit integer.
ToSbyte
- Converts a type to a signed byte type.
ToSingle
- Converts a kind to a small floating factor variety.
ToString
- Converts a type to a string.
ToType
- Converts a kind to a specified type.
ToUInt16
- Converts a type to an unsigned int kind.
ToUInt32
- Converts a type to an unsigned long type.
ToUInt64
- Converts a type to an unsigned big integer.
The following instance converts various price types to thread type
using System;
namespace TypeConversionApplication {
class StringConversion {
static void Main(string[] args) {
int i = 75;
float f = 53.005f;
double d = 2345.7652;
bool b = true;
Console.WriteLine(i.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(f.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(d.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(b.ToString());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}When the above code is compiled and completed, it produces the subsequent result
75 53.005 2345.7652 True
C# programming may be very a great deal primarily based on C and C++ programming languages, so when you have a fundamental understanding of C or C++ programming, then it is going to be fun to examine C#.