Unless you’ve got taken the time configure your browser’s privacy, there’s an amazing chance your browser isn’t always as relaxed as you’ll love it. From place monitoring to nosy cookies to pop-ups — net browsers are shot via with loopholes which could compromise your security in unintentional approaches. If you’ve been considering fortifying your web browser’s security, now is a great time. Here’s the way to do it.
Choose a Secure a Web Browser
The great majority of internet surfers can be found on Chrome, Safari, Firefox, or Internet Explorer. But that does not mean you’re restrained to these picks. There’s thousands of comfortable browser alternatives, along with Iridium browser, GNU IceCat browser, Tor browser, and extra. But no matter which browser you use, keep in mind that there is no such issue as a 100% at ease web browser on its personal. Luckily, you can growth safety on any browser with the aid of locking down the settings and the usage of a VPN (more on that beneath).
Lock Down Your Browser’s Privacy Settings
Have you checked your browser’s settings recently? Configuring your privateness settings is one of the maximum important things you could do to comfy your net browser. By default, many browser settings go away your personal records uncovered. At a minimal, you have to:
- Disable pop-ups and redirections. In addition to being annoying, pop-ups and redirects can be used to spread malicious software.
- Don’t allow automatic downloads. Automatic downloads can contain malware and viruses. Asked to be prompted before downloading anything.
- Keep cookies in check. Delete cookies after browsing and turn off third-party access to cookies.
- Restrict access to your location, camera, and microphone. Set your browser to ask permission before accessing these features.
- Deactivate ActiveX. Active X is considered outdated, and poses security risks. Consider deactivating Flash and Javascript as well.
- Turn on “Send a Do Not Track request.” This will help prevent websites from tracking you, but it’s not guaranteed.

Here’s in which to find your privacy settings on Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, and Safari:
- Chrome privacy settings: Click the “more” ellipsis (three vertical dots) in the top right corner of the browser. Click Settings, then scroll down the page and click Advanced to access your privacy settings.
- Firefox privacy settings. Click the hamburger menu (looks like three vertical lines) in the top right corner of the browser. Select Preferences, then click Privacy & Security.
- Internet Explorer privacy settings: Click the small gear in the right corner of the screen. Click Internet Options, then click the Privacy tab.
- Safari Privacy Settings: Go to Safari > Preferences in the top corner of the browser. Click the Privacy tab to view and update your privacy settings.
Take the time to get familiar with your browser’s unique privacy settings and research extra security suggestions on your browser kind on line. You will likely discover many loopholes you did not realize existed.
Keep Your Web Browser Up-to-Date
Even the most relaxed net browser can’t defend you from the modern-day threats if it’s out-of-date. Every browser is a bit exclusive with regards to software updates. Here’s how updates are treated in Chrome, Firefox, IE, and Safari:
- Google Chrome: Any new updates will trigger automatically whenever you close the browser. To check if Chrome is up-to-date, go to Chrome > About Google Chrome in the top left corner of the browser.
- Firefox: Firefox lets you turn on or off automatic updates under Firefox > Preferences. To check your Firefox version, go to Firefox > About Firefox in the top left corner of the browser.
- Microsoft Internet Explorer: IE updates are distributed through Automatic Updates. To check your IE version, go your computer’s search bar, type in “Internet Explorer,” open the app, click the gear icon, then select About Internet Explorer.
- Apple Safari: To check your Safari version, click Safari > About Safari in the top left corner of the browser. You can also configure Safari extensions to automatically update
Browse In Private or Incognito Mode
While surfing in private mode might not come up with full privateness — your IP cope with and activities can nevertheless be tracked — the usage of private mode prevents your web records, browser cache, form facts, and cookies from being stored once you give up the browser. This means that whoever opens the browser app once you cannot see your browsing records.
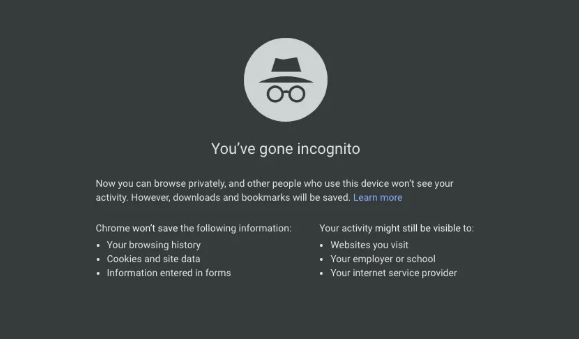
Google Chrome calls non-public browsing Incognito Mode. But you could get entry to private browsing on Firefox and Apple’s Safari browser, too. In Microsoft Internet Explorer, it is known as InPrivate tabs, but works basically similar to all of the different offerings. Your surfing history is protected from prying eyes.
Use Browser Security Extensions
Most browsers provide you with the choice of installing extra security extensions to help bolster your browser security and privateness. When the use of any sort of extension, make certain the extension is advocated with the aid of the browser you’re the usage of, and make sure to permit computerized updates so the extension is constantly up-to-date.
Here are some of the best privacy extensions to get you started:
- HTTPS Everywhere: HTTPS Everywhere works with Firefox, Chrome, and Opera. It works by encrypting your data with many major websites. (By the way, never buy anything from a website that doesn’t use HTTPS!).
- Adblock Plus: AdBlock Plus is an open-source extension for Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, Safari, Edge (beta), Opera, Maxthon, and the Yandex Browser to stop ads from cluttering up your pages and videos.
- Click & Clean: Click & Clean works on Chrome and Firefox that erases your private data, including your browsing history, cache, cookies, passwords, form data, local storage, and more.
- Disconnect: Disconnect works by blocking hundreds of invisible tracker requests inside your browser and apps, which can help to increase page load times. It’s available for Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Opera.
- Privacy Badger: Similar to Disconnect, Privacy Badger works to automatically block invisible website trackers. It’s compatible with Firefox, Opera, and Android.
- Blur: Blur is an excellent privacy tool that works by masking your personal information online, including your email address, phone number, credit card numbers, and more. Blur installs into your browser and works with Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, Opera, and Safari.
You can get Chrome extensions from the Chrome Web Store, Firefox extensions from Firefox Add-ons web page, and Internet Explorer extensions from their Internet Explorer Gallery internet site. You also can simply Google the web browser call plus the phrase “extensions” to quickly locate extensions.
Use a VPN When You Browse the Web

Even the most relaxed browser with the most advanced settings can’t maintain your browsing activities definitely cozy or non-public from your ISP, organisation, or college. That’s why you must consider getting a VPN. A VPN is arms down the best way to relaxed your internet browser, and you ought to bear in mind getting one if privacy and security is crucial to you.
A VPN service protects your web privacy and security in three important ways:
- Disguises your IP address and location: VPNs spoof your IP address and location, so you can’t be tracked by your ISP (internet service provider), search engines, and websites.
- Encapsulates your web traffic: With a VPN, all your data packets are hidden inside additional packets, so your data moves in a private “tunnel” over unsecured networks.
- Encrypts your web traffic: VPN services scramble your data with military-grade encryption, so your data is virtually impossible to hack by outside forces. This is especially important when browsing over public Wi-Fi.
Exercise Common Sense When Browsing
And last however no longer least, exercising commonplace sense while browsing the internet. Even with the most relaxed browser and VPN, malicious websites can trick you into clicking on malicious hyperlinks or downloading malware. Be wary of shortened links (e.G., bit.Ly) that can disguise bad links, and avoid non-HTTPS web sites whenever possible. And lastly, by no means allow downloads or installation software program unless it’s from a trusted website.