Microsoft’s hard circle filtering and repair utility, Windows CHKDSK (“check plate”), was presented more than 30 years back yet at the same time has a helpful place today. Clients running even the most recent Microsoft working framework can in any case utilize the command to look at their hard drives for mistakes and repair them if fundamental. So lets check disk on windows using CHKDSK.
Open Command Prompt
Indeed, even in Windows 10, the CHKDSK command is run by means of the Command Prompt, yet we’ll have to utilize regulatory privileges to appropriately get to it. To dispatch a Command Prompt as an Administrator, press the console alternate way Windows Key + X to raise the power clients menu, at that point let go of those two keys and tap the A key. On the other hand, with the power clients menu open you can utilize your mouse or trackpad to choose the Command Prompt (Admin) alternative.

Allow the cmd to make changes!!
You’ll be given a UAC window asking for authorization to dispatch the Command Prompt as Administrator. Snap Yes to continue and you’ll see another Command Prompt window. You can verify that you’ve effectively allowed the Command Prompt authoritative privileges by guaranteeing that “Manager: Command Prompt” is available in the window’s title bar.
From the Command Prompt, type the command “chkdsk” trailed by a space, at that point the letter of the drive you wish to look at or repair. For our situation, it’s inside drive “C.”
Lets type some COMMANDS!!
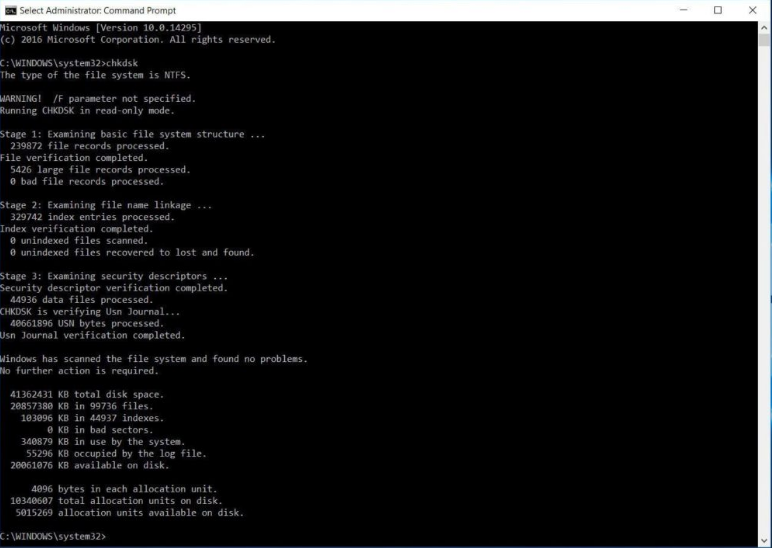
Basically running the CHKDSK command in Windows 10 will just show the circle’s status, and won’t settle any blunders present on the volume. To advise CHKDSK to settle the drive, we have to give it parameters. After your drive letter, type the accompanying parameters isolated by a space each: “/f/r/x”.
The “/f” parameter advises CHKDSK to settle any mistakes it finds; “/r” instructs it to find the awful divisions on the drive and recuperate lucid data; “/x” powers the drive to get off before the procedure begins. Extra parameters are accessible for more particular assignments, and are nitty gritty at Microsoft’s site.
To abridge, the full command that ought to be composed into the Command Prompt is:
[cc]chkdsk [Drive:] [parameters][/cc]
In our precedent, it’s:
[cc]chkdsk C: /f /r /x[/cc]
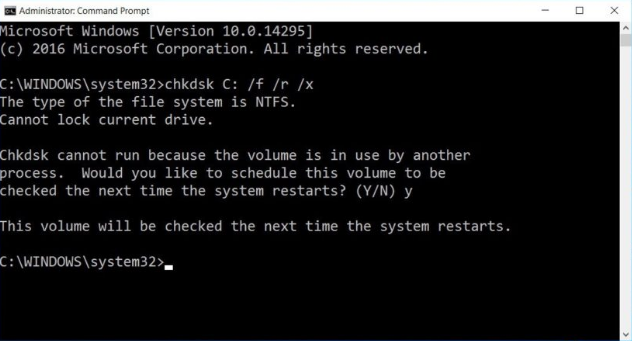
Note that CHKDSK should have the capacity to bolt the drive, implying that it can’t be utilized to look at the framework’s boot drive if the PC is being used. If your objective drive is an outer or non-boot inside plate, the CHKDSK procedure will start when we enter the command above.
Lets restart
If, be that as it may, the objective drive is a boot circle, the framework will inquire as to whether you’d get a kick out of the chance to run the command before the following boot. Sort “yes” (or “y”), restart the PC, and the command will keep running before the working framework loads, enabling it to increase full access to the disk.
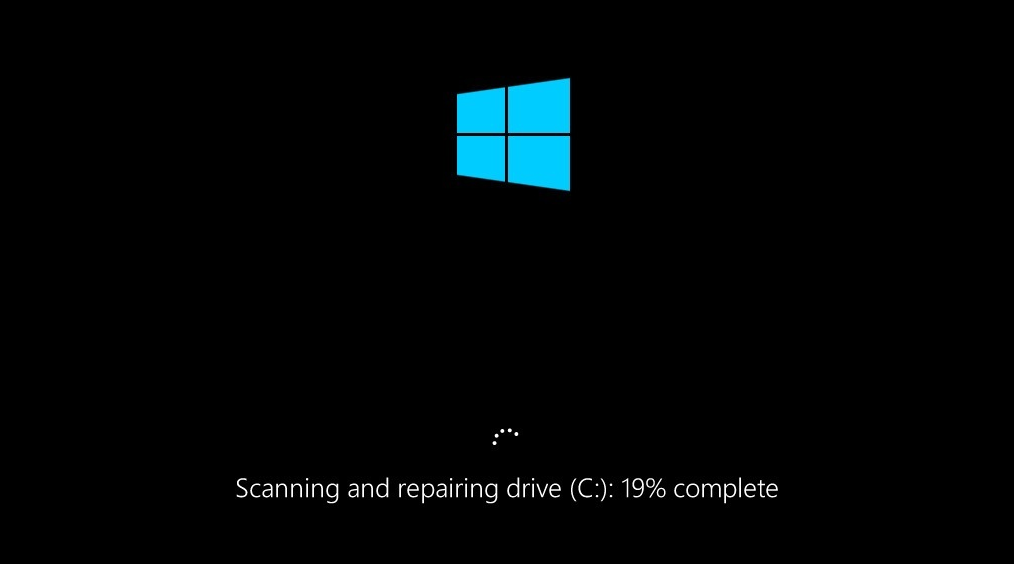
A CHKDSK command can take quite a while, particularly when performed on bigger drives. When it’s set, be that as it may, it will introduce an outline of results including complete plate space, byte allotment, and, in particular, any blunders that were found and redressed.
The CHKDSK command is accessible in all variants of Windows, so those on Windows 7, 8, or XP can likewise play out the means above to start a sweep of their hard drive. On account of more seasoned adaptations of Windows, clients can get to the Command Prompt by going to Start > Run and composing “cmd”. When the Command Prompt outcome is shown, right-tap on it and select “Keep running as Administrator” to concede the program the important privileges to execute CHKDSK effectively.




